Second Equation of motion, How to implement using C language
The second equation of motion is used to calculate the displacement of an object under constant acceleration.
want to check the implementation of the Third equation of motion, click here.
The second equation of motion is
s = u*t + 1/2 * a * t * t
s: total displacement
u: initial velocity
t: time taken by the journey
a: constant acceleration
as you can see in our program we are considering u=0 if you want you can set initialVelocity variable value as per your choice or you can ask it from user too also acceleration value is 9.8 equal to the gravity of earth.
want to check the implementation of the first equation of motion, click here.
In a function fallingDistance we have implemented the equation.
total_dist = 9.8 * i * i * 1/2 + u * i ;
total_dist = (4.9 * i * i) + (u * i);
Code:
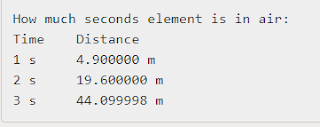
The sample output of this code is.
Want to check the implementation of first equation of motion.
Thanks for reading this, for any implementation please ask in the comment section.
want to check the implementation of the Third equation of motion, click here.
want to check the implementation of second equation of motion, click here.
Algorithm:
Without wasting any of your precious time let's try to understand how the algorithm is implemented.want to check the implementation of the Third equation of motion, click here.
The second equation of motion is
s = u*t + 1/2 * a * t * t
s: total displacement
u: initial velocity
t: time taken by the journey
a: constant acceleration
as you can see in our program we are considering u=0 if you want you can set initialVelocity variable value as per your choice or you can ask it from user too also acceleration value is 9.8 equal to the gravity of earth.
want to check the implementation of the first equation of motion, click here.
In a function fallingDistance we have implemented the equation.
total_dist = 9.8 * i * i * 1/2 + u * i ;
total_dist = (4.9 * i * i) + (u * i);
Code:
#include
// this is the implementation of 2nd equations of motion.
void fallingDistance(int x,float u){
float total_dist=0;
printf("Time\tDistance\n");
for (int i=1;i<=x;i++){
total_dist = (4.9 * (i*i)) + (u * i);
printf("%d s\t%f m\n",i,total_dist);
}
}
int main() {
int fallingTime=0;
int initialVelocity=0;
//printf("How much is the initial Velocity of element:");
//scanf("%f",&initialVelocity);
printf("How much seconds element is in air:");
scanf("%d",&fallingTime);
printf("\n");
fallingDistance(fallingTime,initialVelocity);
return 0;
}
The sample output of this code is.
Want to check the implementation of first equation of motion.
Thanks for reading this, for any implementation please ask in the comment section.
want to check the implementation of the Third equation of motion, click here.
want to check the implementation of second equation of motion, click here.



Comments
Post a Comment